GridTrust: Electricity Grid Root-of-Trust Decentralized Supply Chain Cyber-Security
Disclaimer: This page is a work-in-progress and code is not yet available.
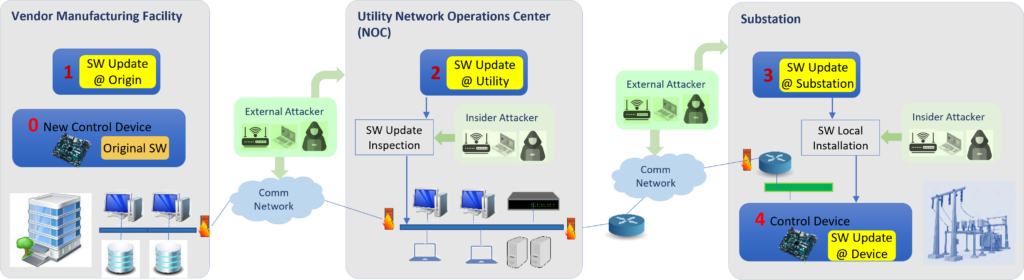
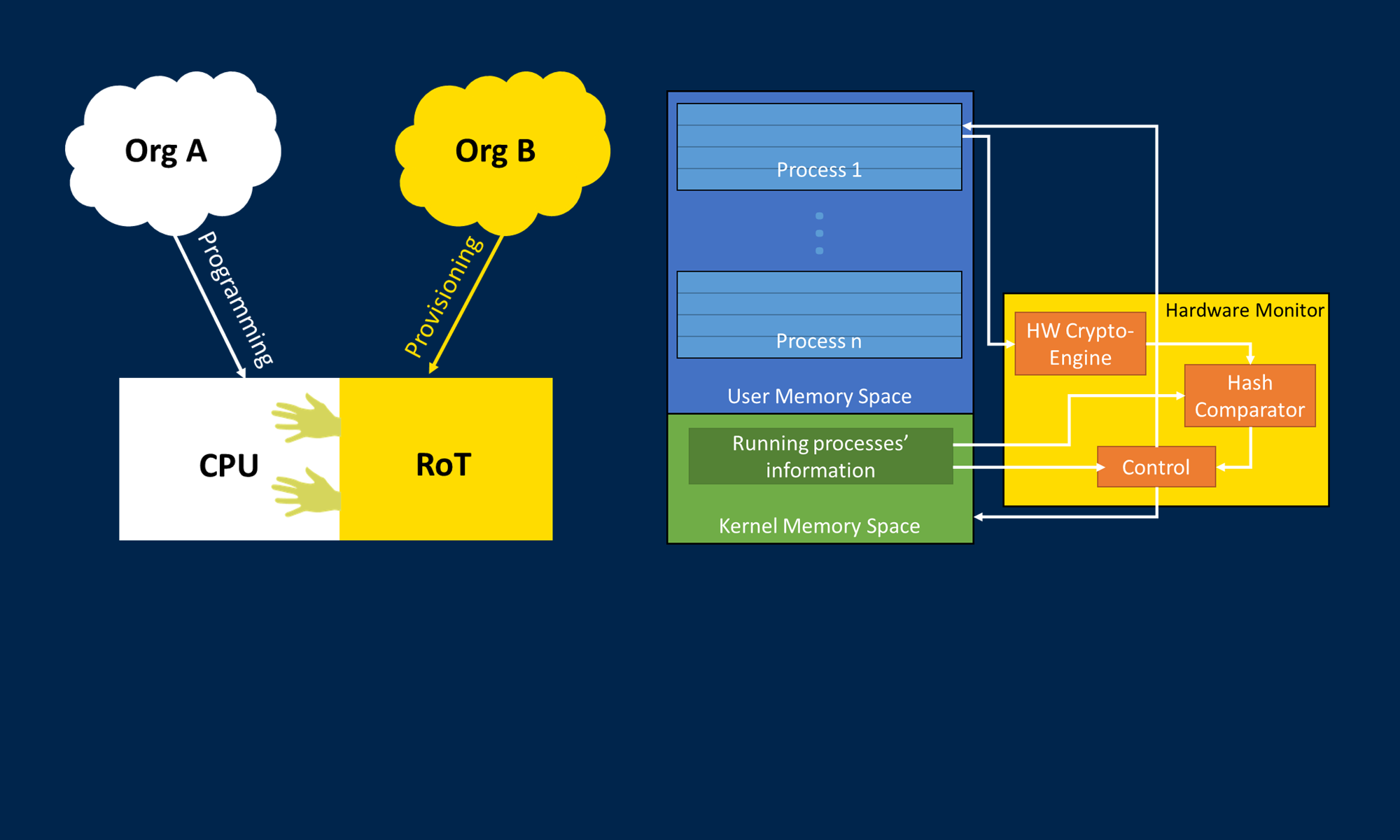
Hardware/software co-designed systems are increasingly prevalent due to trends such as the adoption of hardware accelerators and the availability of heterogeneous system-on-chip (SoC) architectures. A potential security concern arising from hardware/software interaction in heterogeneous computing architectures is the possibility of software-based attacks on reconfigurable hardware, and vice versa. This is especially important when considering remote updates of the software, hardware, or both combined. In this work, we have created a remote update scheme that relies on a physical unclonable function (PUF) and multiple updating parties to deliver hardware/software updates in a secure fashion. The scheme, GridTrust, provides a high level of assurance that the system only accepts updates from approved entities while also preventing common remote attacks from compromising the security of the update process. As shown above, an attacker has multiple opportunities to attack. GridTrust’s protection features help to prevent any single attack from the locations shown in Figure 1 from succeeding.
The GridTrust scheme follows a few key tenets; (1) the usage of auditable open-source software, (2) software update authorization via two distinct entities, (3) and device authentication via a hardware fingerprinting technique known as a PUF. Used together, these techniques harden cybersecurity defenses in the electric grid supply chain against both a third-party actor and a malicious lone-wolf insider.
Collaborators
Publications
- J. Keller, S. Paul, K. Hutto, S. Grijalva, V. Mooney, “Developing Simulation Capabilities for Supply Chain Cybersecurity of the Electricity Grid,” 2023 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Latin America, November 2023.
J. Keller, S. Paul, S. Grijalva, V. Mooney, “Experimental Setup for Grid Control Device Software Updates in Supply Chain Cyber-Security,” 2022 54th North American Power Symposium (NAPS’22), October 2022. Presentation (pdf)
K. Hutto, S. Paul, B. Newberg, V. Boyapati, Y. Vunnam, S. Grijalva, V. Mooney, “PUF-Based Two-Factor Authentication Protocol for Securing the Power Grid Against Insider Threat,” Kansas Power and Energy Conference (KPEC’22), April 2022. Presentation (pdf)
B. Newberg, S. Grijalva, V. Mooney, “Open-Source Architecture for Multi-Party Update Verification for Data Acquistion Devices,” Power and Energy Conference at Illinois, March 2022. Presentation (pdf)
K. Hutto, S. Grijalva, V. Mooney, “Hardware-Based Randomized Encoding for Sensor Authentication in Power Grid SCADA Systems,” 2022 Texas Power and Energy Conference, February 2022. Presentation (pdf)
Contact Info
- For questions please contact Kevin Hutto at khutto30@gatech.edu
Support
This work was supported in part by The US Department of Energy
Office of Cyber-Security, Energy Security and Emergency Response (CESER),
Cybersecurity for Energy Delivery Systems (CEDS) Award to the Georgia
Institute of Technology, # DE-CR0000004.